When selecting an Industrial Gas Generator, understanding your specific needs is crucial. John Smith, a leading expert in the field, once stated, "Choosing the right generator can make or break your operational efficiency." This emphasizes the importance of thorough research before making a decision.
An Industrial Gas Generator must match your power requirements, fuel availability, and environmental factors. Every business has unique demands. A generator that works for one might not be suitable for another. Additionally, consider the maintenance and operational cost involved. Sometimes, the less expensive option leads to greater expenses down the line.
It’s easy to overlook small details that can have a significant impact. For instance, noise levels and emissions should not be ignored. These factors can affect your business's reputation and relationships with local communities. An informed choice today can lead to smoother operations tomorrow. Finding the ideal Industrial Gas Generator is a balance of many elements. Be prepared to reflect and rethink your choices for better outcomes.

When selecting an industrial gas generator, it’s crucial to understand the types available. There are two main categories: portable and stationary units. Portable generators can be moved easily. This mobility is beneficial for temporary projects or remote sites. On the other hand, stationary units are more suitable for permanent installations. They offer higher power outputs and can support larger operations.
Different fuels can power these generators. Natural gas is popular for its efficiency and lower emissions. Propane is another option, offering good performance and storage convenience. Diesel generators, while not gas-powered, are often included in discussions. They provide robust power but come with higher emissions. Each fuel type has its pros and cons.
Buying a generator isn't just about power needs. Size, noise level, and maintenance must be considered. Some units may be too loud for certain environments. It's worth reflecting on how the generator fits into your broader operation. Choosing the perfect generator can be overwhelming. Each option requires careful thought, ensuring it aligns with your specific needs.
This chart illustrates the comparison of different types of industrial gas generators based on their power output and fuel efficiency ratings. As companies look to choose the best generator for their specific needs, understanding these metrics can help make an informed decision.
When selecting an industrial gas generator, it’s crucial to consider key performance metrics. These metrics often include efficiency, output capacity, and emissions profile. A recent report by the International Energy Agency indicates that efficiency matters greatly. Generators with 90% efficiency or higher can drastically reduce operational costs.
Output capacity is another significant factor. An underpowered generator can lead to productivity loss. According to industry studies, businesses should choose models that offer 20% more capacity than their peak demand. Emission profiles also require attention. Many industrial sectors now prioritize sustainability. Generators that minimize NOx and CO emissions can help companies comply with environmental regulations.
However, evaluating these metrics is not always straightforward. Some generators may claim high efficiency but underperform in real-world conditions. Furthermore, noise levels can be overlooked in performance evaluations. A generator might meet efficiency standards yet create excessive noise, impacting work environments. Companies must weigh these factors carefully to make well-informed choices.
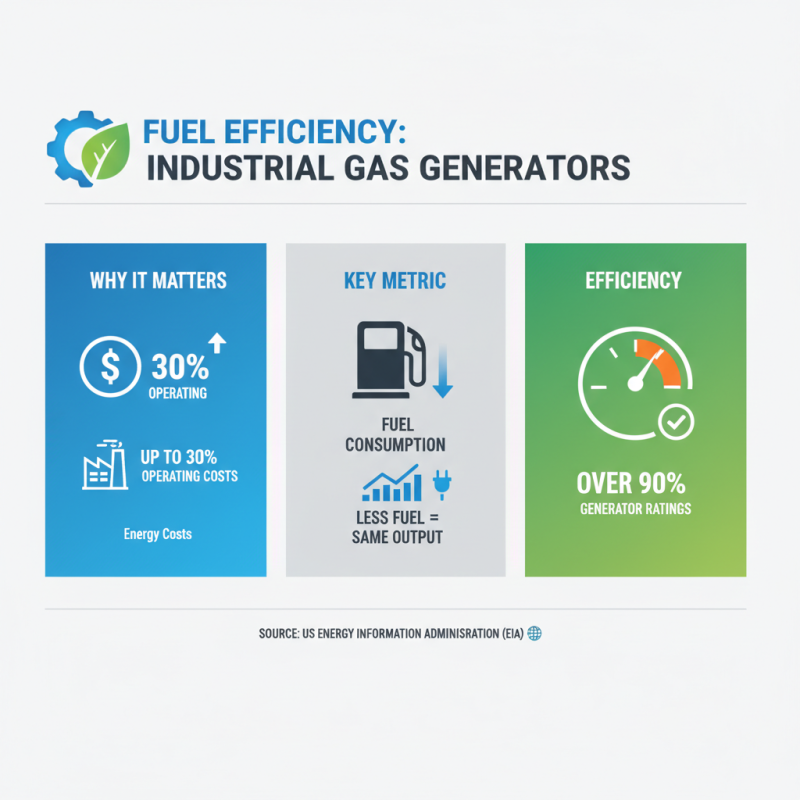
When selecting an industrial gas generator, fuel efficiency is crucial. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, energy costs can account for up to 30% of a facility's operating expenses. Therefore, understanding fuel consumption is vital. Some gas generators can achieve efficiency ratings of over 90%. This means less fuel is needed for the same output.
Operational costs encompass more than just fuel. Regular maintenance can help optimize efficiency. For instance, a study from the International Energy Agency found that neglected maintenance could increase energy costs by 20%. Ensure that you have a maintenance schedule to avoid these pitfalls.
Tips: Always compare the fuel consumption rates of different generators. Look for models with advanced technologies that enhance efficiency. Evaluate the total cost over their lifespan, factoring in repairs and maintenance. Remember, investing in a high-efficiency generator from the start can lead to significant savings in the long run.
Choosing the right generator size is crucial for efficiency. Understanding the power requirements is the first step. According to industry reports, there is a common miscalculation of necessary wattage. Many underestimate their needs, resulting in inadequate power supply.
For instance, a typical construction site may require around 10,000 watts for tools and machinery. However, many operators may opt for a smaller generator, assuming they can save costs. This can lead to interruptions in work and increased operational delays. Efficiency reports indicate that underpowering can increase fuel costs by up to 30%. This is a significant oversight.
Another point to consider is the startup surge of equipment. Certain tools require more power during startup than their running wattage suggests. Ignoring this surge can lead to generator overload or failure. Properly sizing a generator is not just about current needs; it’s about planning for unexpected demands as well. An analysis of historical data from various industries shows that proper sizing can reduce operational risks and enhance overall productivity.
| Generator Size (kW) | Suggested Applications | Typical Fuel Consumption (L/hr) | Noise Level (dB) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | Small workshops, mobile units | 1.5 | 65 | 120 |
| 25 | Construction sites, medium workshops | 3.0 | 70 | 250 |
| 50 | Larger industrial applications, events | 5.5 | 75 | 500 |
| 100 | Manufacturing plants, data centers | 12.0 | 80 | 900 |
| 200 | Hospital backup, data centers | 30.0 | 85 | 1500 |
When selecting an industrial gas generator, regulatory standards are crucial. Various industries must adhere to local and international regulations concerning emissions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), gas generators emit less than 25 tons of CO2 annually. This lower emission standard makes them preferable for many operations. However, these regulations can vary significantly regionally, requiring diligence in compliance.
Environmental considerations are equally important. Gas generators typically produce fewer particulate emissions than diesel counterparts. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that natural gas-fired generators can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50%. Yet, some issues persist. Even with cleaner technologies, there are concerns about methane leaks during extraction and transport. These leaks can undermine the environmental benefits, leading to calls for better oversight.
Potential users must reflect on these factors. Balancing operational needs with environmental responsibilities is challenging. While focusing on efficiency, remember to evaluate generator contingency plans for compliance failures. The stakes are high. Neglecting regulations can lead to hefty fines and regulatory scrutiny. An informed choice of a gas generator must consider these multifaceted aspects without falling into the trap of mere compliance.






